Navigating Legal Frontiers in Space Mining: Key Considerations
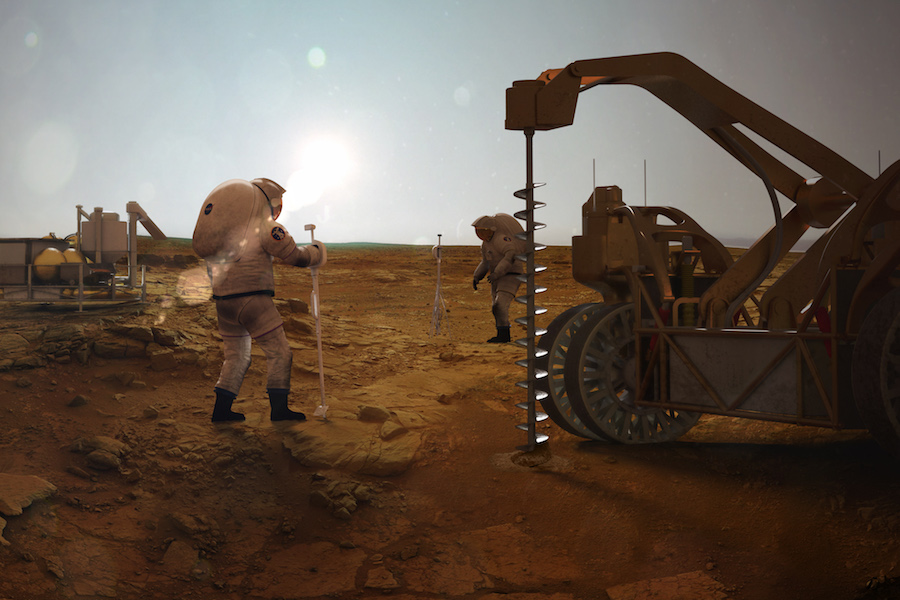

Exploring the Legal Landscape of Space Mining
Introduction to Space Mining:
As humanity ventures into the cosmos, the concept of space mining has emerged as a frontier with vast potential. This article delves into the legal considerations surrounding space mining, addressing the complexities and challenges that arise as we seek to harness resources beyond Earth.
International Space Law Framework:
The legal foundation for space activities is primarily governed by international agreements. The Outer Space Treaty, established by the United Nations, serves as a cornerstone. Understanding the framework set by international space law is crucial in navigating the legal aspects of space mining and ensuring responsible exploration and utilization of celestial resources.
Property Rights and Ownership in Outer Space:
One of the central legal challenges in space mining revolves around property rights. The Outer Space Treaty prohibits national appropriation of celestial bodies, but it doesn’t explicitly address ownership of extracted resources. Legal frameworks must evolve to provide clarity on property rights, defining how companies can use and benefit from mined materials without violating international agreements.
Regulating Space Mining Activities:
Regulating space mining activities requires a delicate balance between encouraging innovation and safeguarding celestial environments. Legal considerations involve establishing licensing and permitting processes to authorize space mining ventures. Regulators must ensure compliance with environmental protection standards and prevent activities that could jeopardize other space missions or celestial bodies.
Environmental and Celestial Body Protection:
Preserving the pristine environments of celestial bodies is a priority in space mining legal considerations. Legal frameworks should include measures to prevent contamination, mitigate space debris, and protect celestial bodies from undue harm. Striking a balance between resource extraction and environmental preservation requires thoughtful legislation.
Avoiding Harmful Interference:
Legal safeguards must be in place to prevent harmful interference with other space activities. As the number of space mining ventures increases, the potential for conflicts and interference rises. Clear regulations on communication, coordination, and dispute resolution are essential to ensure the peaceful coexistence of diverse space endeavors.
Benefit-Sharing and International Collaboration:
The equitable distribution of benefits derived from space mining activities is a critical legal consideration. International collaboration is essential to establish frameworks for benefit-sharing among nations. Legal agreements should outline how the advantages of space mining will be shared to promote fair and inclusive participation in the benefits of celestial resource utilization.
Liability and Space Mining Accidents:
Legal frameworks for space mining must address liability in the event of accidents or damage. Establishing liability regimes ensures that companies are held accountable for any harm caused during space mining activities. Defining responsibility and compensation mechanisms is crucial to protect the interests of all parties involved.
Technological Innovation and Legal Adaptation:
The rapid pace of technological innovation in space mining necessitates legal adaptation. Legal frameworks must be flexible enough to accommodate emerging technologies while maintaining a clear regulatory structure. Ongoing dialogue between legal experts and space industry stakeholders is crucial to ensure that regulations evolve alongside technological advancements.
Public and Private Sector Collaboration:
Space mining involves both public and private sector entities. Legal considerations should encourage collaboration while safeguarding public interests. Balancing the competitive nature of private ventures with the broader goals of humanity in space exploration requires legal frameworks that promote cooperation and responsible conduct.
Education and Advocacy for Space Legal Literacy:
The complex nature of space mining legal considerations calls for enhanced education and advocacy efforts. Legal professionals, policymakers, and the public need to develop space legal literacy to contribute meaningfully to the ongoing dialogue. Education initiatives should focus on raising awareness of the legal challenges and opportunities in space mining.
In conclusion, the legal considerations in space mining are integral to shaping a sustainable and responsible future in celestial resource utilization. For a comprehensive exploration of Legal Considerations in Space Mining, visit StarMountainResources.com.
As we venture into the cosmos, the legal frameworks established today will shape the future of space mining, ensuring that it aligns with international norms, benefits humanity as a whole, and preserves the wonders of outer space for generations to come.