Navigating E-commerce Regulations: Legal Compliance in Digital Markets

The Complex World of E-commerce Regulations
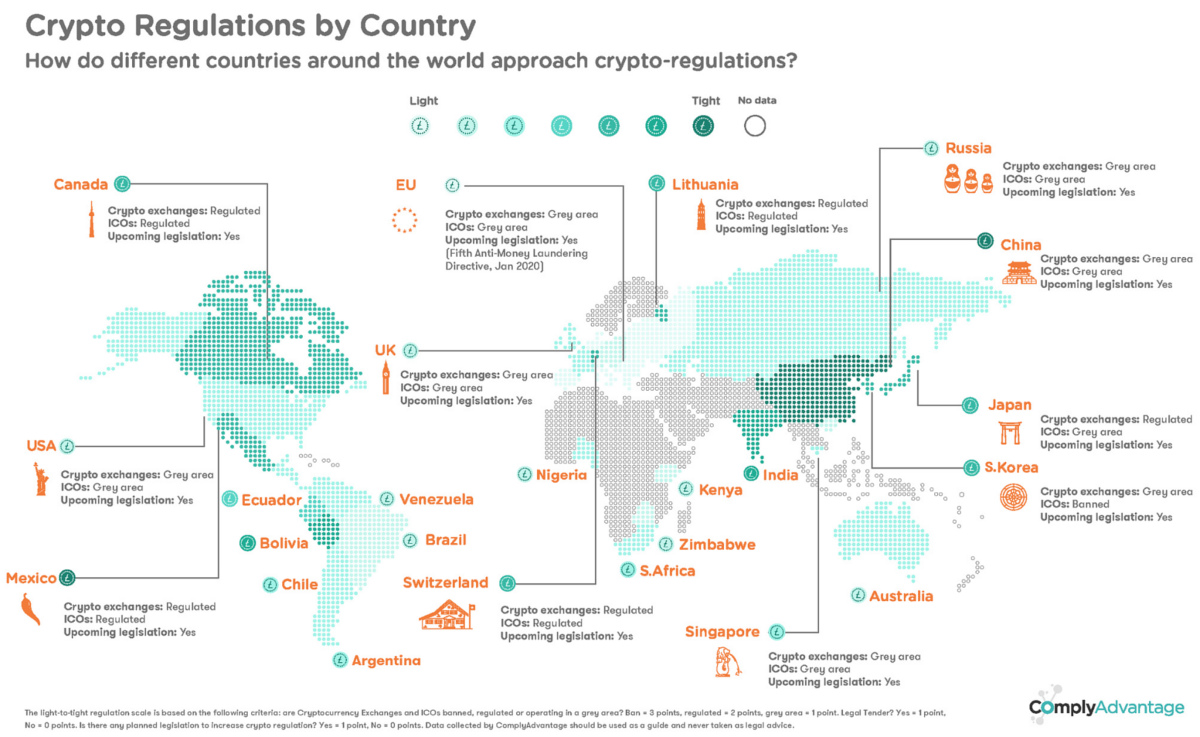
E-commerce has witnessed explosive growth, becoming a cornerstone of the modern economy. With this surge comes the need for robust regulations to ensure fair practices, protect consumers, and foster a healthy digital marketplace.
The Evolution of E-commerce Regulations
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so do the regulations governing e-commerce. Governments globally are adapting their legal frameworks to keep pace with the rapid advancements in online business models, data protection, and consumer rights.
Consumer Protection in E-commerce
One of the primary focuses of e-commerce regulations is consumer protection. Legal standards are established to safeguard consumers from fraudulent activities, ensure transparent business practices, and guarantee fair dispute resolution mechanisms. These regulations aim to build trust in online transactions.
Data Privacy and Security Measures
In an era where data is a valuable commodity, regulations address the critical aspects of data privacy and security in e-commerce. Compliance requirements ensure that businesses handle customer data responsibly, protecting it from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Cross-Border E-commerce Challenges
With the global nature of e-commerce, cross-border transactions are common. However, this presents challenges in terms of varying regulations across jurisdictions. Harmonizing international e-commerce regulations becomes essential to facilitate seamless cross-border trade.
Digital Payments and Financial Regulations
As e-commerce relies heavily on digital payments, regulations in this domain are crucial. Financial regulations ensure the security and reliability of payment systems, protect against fraud, and foster innovation in financial technology to enhance the e-commerce payment landscape.
Platform Liability and Accountability
E-commerce platforms play a central role in facilitating transactions. Regulations are evolving to define the liability and accountability of these platforms, balancing their responsibilities in monitoring content, ensuring product authenticity, and addressing issues such as counterfeiting.
Intellectual Property Protection
E-commerce platforms are breeding grounds for the sale of various goods, raising concerns about intellectual property infringement. Regulations are designed to protect trademarks, copyrights, and patents, providing legal recourse for rights holders against unauthorized use.
Environmental Sustainability in E-commerce
With the rise of online shopping, concerns about the environmental impact of packaging and shipping have surfaced. E-commerce regulations are now beginning to address sustainability issues, encouraging eco-friendly practices in packaging and logistics.
Compliance Challenges for Businesses
For businesses engaged in e-commerce, navigating the complex web of regulations poses challenges. Staying compliant with evolving standards requires constant vigilance and adaptability. Businesses must invest in legal counsel and compliance measures to mitigate risks and ensure sustained growth.
Exploring E-commerce Regulations Further
For a deeper understanding of the intricacies of e-commerce regulations, explore resources such as E-commerce regulations. This platform offers valuable insights into the evolving legal landscape of e-commerce, helping businesses and stakeholders stay informed and compliant in the dynamic world of digital trade.