Navigating Data Localization Laws: Global Compliance Strategies
Navigating Data Localization Laws: Global Compliance Strategies
Introduction to Data Localization Laws
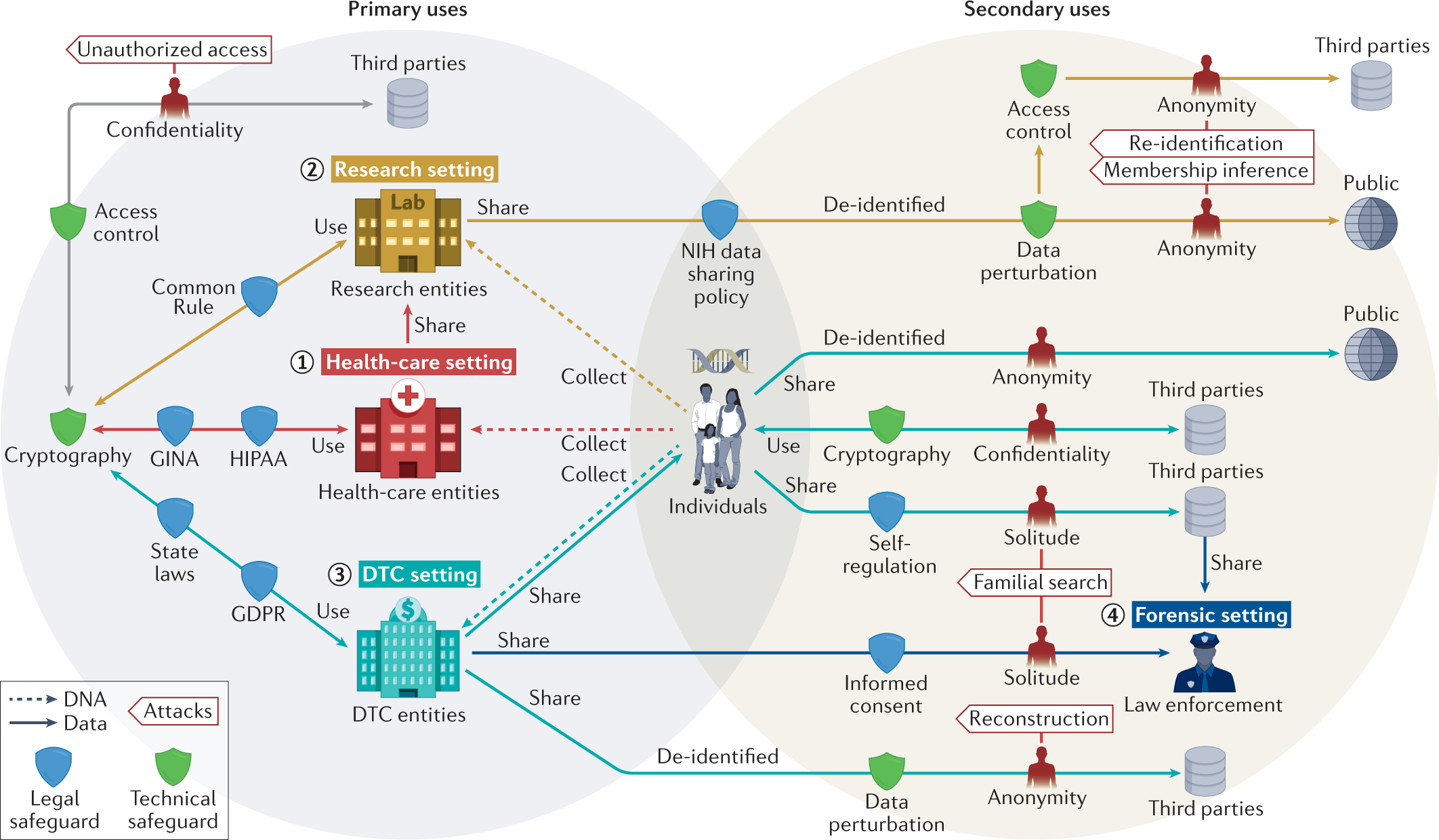
In an interconnected world, data flows seamlessly across borders, but concerns over privacy and national security have led to the emergence of data localization laws. These regulations mandate that certain data must be stored within a specific geographic location, posing challenges and opportunities for businesses operating globally. This article explores the intricacies of data localization laws and provides strategies for achieving global compliance.
The Rationale Behind Data Localization
Governments enact data localization laws to address various concerns, including data privacy, national security, and the protection of sensitive information. Understanding the motivations behind these regulations is crucial for businesses seeking to navigate the evolving landscape of data governance. Compliance involves aligning operations with the specific requirements set forth by each jurisdiction.
Challenges Faced by Businesses
Data localization presents challenges for businesses with global operations. Complying with diverse and sometimes conflicting regulations requires a nuanced approach. Challenges include the complexity of legal landscapes, the need for significant operational adjustments, and potential impacts on the cost and efficiency of data management. Businesses must assess these challenges to develop effective compliance strategies.
Navigating Jurisdictional Variations
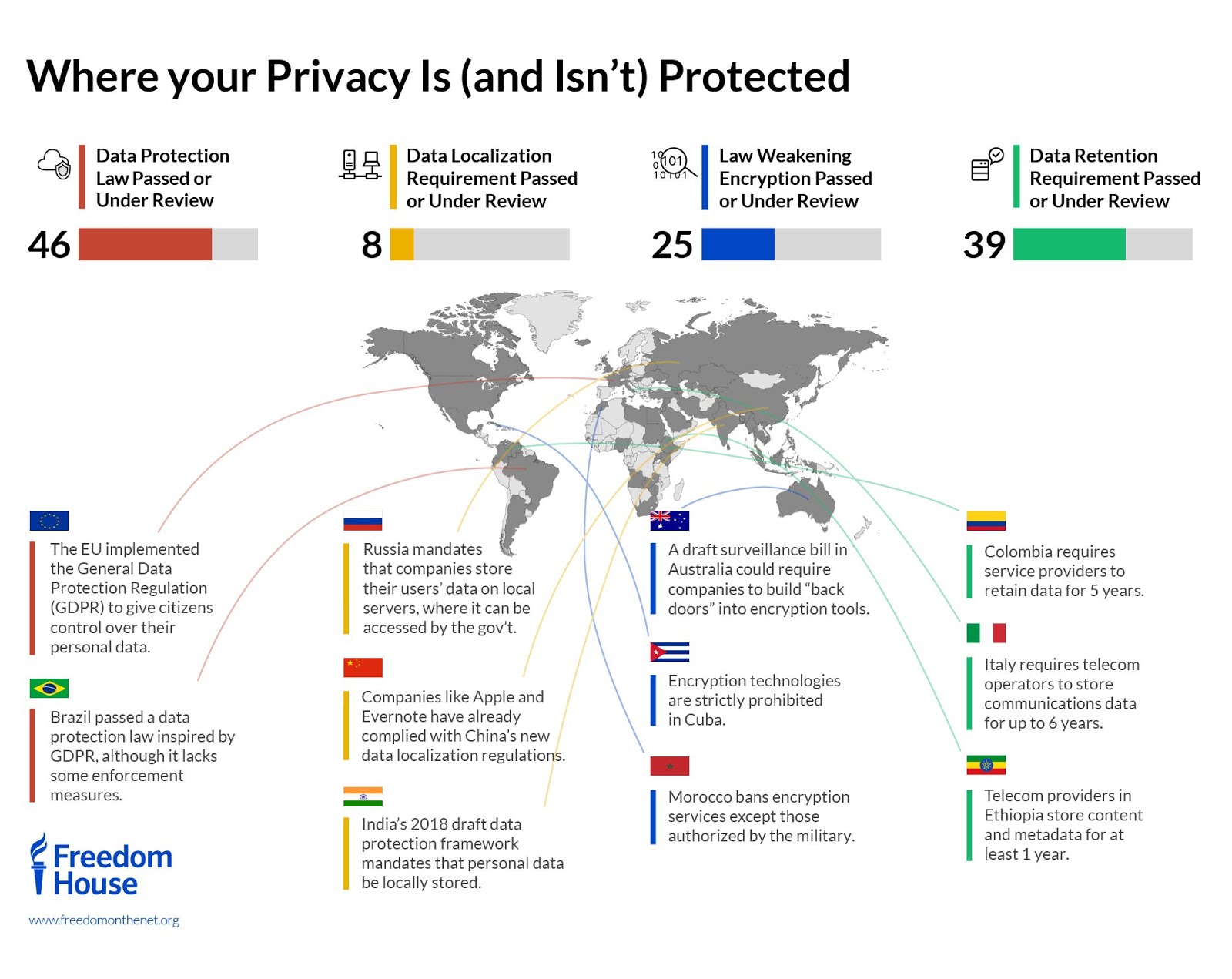
Data localization laws vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. Some countries have strict requirements, while others adopt more flexible approaches. Navigating these jurisdictional variations demands a comprehensive understanding of local regulations, ensuring that businesses can tailor their compliance strategies to align with specific legal frameworks.
Strategies for Global Compliance
Achieving global compliance with data localization laws involves implementing strategic measures. One approach is to adopt a data mapping strategy, identifying the types of data subject to localization requirements. Cloud-based solutions with regional data centers can also facilitate compliance by ensuring that data is stored in accordance with relevant regulations. Collaborating with legal experts in each jurisdiction further strengthens compliance efforts.
The Role of Encryption and Security Measures
Encryption plays a pivotal role in data localization compliance. Implementing robust encryption measures enhances data security and aligns with the principles of many localization regulations. Businesses should prioritize cybersecurity measures to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality, thereby meeting both legal requirements and international best practices.
Cross-Border Data Transfers and Consent Management
Navigating data localization laws involves managing cross-border data transfers effectively. Obtaining informed consent from data subjects is a critical component. Implementing transparent consent mechanisms ensures compliance while maintaining the trust of users. Businesses should adopt user-friendly approaches to consent management, providing clear information about how and where data will be stored.
Impact on Cloud Service Providers
Data localization laws also impact cloud service providers (CSPs). These providers must adapt their infrastructure to comply with varying regulations across jurisdictions. Businesses leveraging cloud services should collaborate closely with CSPs to ensure alignment with data localization requirements, mitigating potential legal and operational risks.
Monitoring Regulatory Updates
The landscape of data localization laws is dynamic, with regulations subject to frequent updates and amendments. Businesses must establish robust mechanisms for monitoring regulatory changes in each jurisdiction where they operate. This proactive approach enables timely adjustments to compliance strategies, ensuring that businesses stay ahead of evolving legal requirements.
Data Localization Laws Resource
For businesses seeking comprehensive insights into data localization laws and global compliance strategies, Data localization laws serves as a valuable resource. This platform provides updates on regulatory developments, practical guidance, and industry best practices. Staying informed through such resources is essential for businesses navigating the complexities of data governance on a global scale.
Conclusion: Adapting to the Data Localization Era
As data localization laws continue to shape the regulatory landscape, businesses must adapt to this new era of data governance. Global compliance requires a strategic and proactive approach, encompassing legal expertise, technological solutions, and a commitment to respecting the privacy and security of user data. Navigating the complexities of data localization ensures that businesses not only meet legal requirements but also foster trust in an increasingly interconnected digital world.